What Are the Best Practices for Web Scraping?
Advanced Data Extraction Specialist
Introduction: A New Paradigm of Browser Automation and Data Collection in the AI Era
With the rapid rise of generative AI, AI agents, and data-intensive applications, browsers are evolving from traditional "user interaction tools" into "data execution engines" for intelligent systems. In this new paradigm, many tasks no longer rely on single API endpoints but instead leverage automated browser control to handle complex page interactions, content scraping, task orchestration, and context retrieval.
From price comparisons on e-commerce sites and map screenshots to search engine result parsing and social media content extraction, the browser is becoming a crucial interface for AI to access real-world data. However, the complexity of modern web structures, robust anti-bot measures, and high concurrency demands pose significant technical and operational challenges for traditional solutions like local Puppeteer/Playwright instances or proxy rotation strategies.
Enter the Scrapeless Scraping Browser—an advanced, cloud-based browser platform purpose-built for large-scale automation. It overcomes key technical barriers such as anti-scraping mechanisms, fingerprint detection, and proxy maintenance. Furthermore, it offers cloud-native concurrency scheduling, human-like behavior simulation, and structured data extraction, positioning itself as a vital infrastructure component in the next generation of automation systems and data pipelines.
This article explores the core capabilities of Scrapeless and its practical applications in browser automation and web scraping. By analyzing current industry trends and future directions, we aim to provide developers, product builders, and data teams with a comprehensive and systematic guide.
I. Background: Why Do We Need Scrapeless Scraping Browser?
1.1 The Evolution of Browser Automation
In the AI-driven automation era, browsers are no longer just tools for human interaction—they have become essential execution endpoints for acquiring both structured and unstructured data. In many real-world scenarios, APIs are either unavailable or limited, making it necessary to simulate human behavior via browsers for data collection, task execution, and information extraction.
Common use cases include:
- Price comparison on e-commerce sites: Price and stock data are often loaded asynchronously in the browser.
- Parsing search engine result pages: Content must be fully loaded by scrolling and clicking on page elements.
- Multilingual websites, legacy systems, and intranet platforms: Data access is impossible via API.
Traditional scraping solutions (e.g., locally run Puppeteer/Playwright or proxy rotation setups) often suffer from poor stability under high concurrency, frequent anti-bot blocking, and high maintenance costs. Scrapeless Scraping Browser, with its cloud-native deployment and real browser behavior simulation, provides developers with a high-availability, reliable browser automation platform—serving as critical infrastructure for AI automation systems and data workflows.
1.2 The Challenge of Anti-Bot Mechanisms
At the same time, as anti-bot technologies evolve, traditional crawler tools are increasingly flagged as bot traffic by target websites, resulting in IP bans and access restrictions. Common anti-scraping mechanisms include:
- Browser fingerprinting: Detects abnormal access patterns via User-Agent, canvas rendering, TLS handshake, and more.
- CAPTCHA verification: Requires users to prove they are human.
- IP blacklisting: Blocks IPs that access too frequently.
- Behavioral analysis algorithms: Detect unusual mouse movement, scroll speeds, and interaction logic.
Scrapeless Scraping Browser effectively overcomes these challenges through precise browser fingerprint customization, built-in CAPTCHA solving, and flexible proxy support—becoming core infrastructure for the next generation of automation tools.
II. Core Capabilities of Scrapeless
The Scrapeless Scraping Browser delivers powerful core capabilities, offering users stable, efficient, and scalable data interaction features. Below are its main functional modules and technical details:
2.1 Real Browser Environment
Scrapeless is built on the Chromium engine, providing a complete browser environment capable of simulating real user behavior. Key features include:
- TLS fingerprint spoofing: Fakes TLS handshake parameters to bypass traditional anti-bot mechanisms.
- Dynamic fingerprint obfuscation: Adjusts User-Agent, screen resolution, timezone, etc., to make each session appear highly human-like.
- Localization support: Customize language, region, and timezone settings to make interactions with target websites more natural.
Deep Customization of Browser Fingerprints
Scrapeless offers comprehensive customization of browser fingerprints, allowing users to create more "authentic" browsing environments:
- User-Agent control: Define the User-Agent string in browser HTTP requests, including browser engine, version, and OS.
- Screen resolution mapping: Set the return values of
screen.widthandscreen.heightto simulate common display sizes. - Platform property locking: Specify the return value of
navigator.platformin JavaScript to simulate the operating system type. - Localized environment emulation: Fully supports custom localization settings, affecting content rendering, time format, and language preference detection on websites.
2.2 Cloud-Based Deployment and Scalability
Scrapeless is fully deployed in the cloud and offers the following advantages:
- No local resources required: Reduces hardware costs and improves deployment flexibility.
- Globally distributed nodes: Supports large-scale concurrent tasks and overcomes geographic restrictions.
- High concurrency support: From 50 to unlimited concurrent sessions—ideal for everything from small tasks to complex automation workflows.
Performance Comparison
Compared with traditional tools such as Selenium and Playwright, Scrapeless excels in high-concurrency scenarios. Below is a simple comparison table:
| Feature | Scrapeless | Selenium | Playwright |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concurrency Support | Unlimited (Enterprise-grade customization) | Limited | Moderate |
| Fingerprint Customization | Advanced | Basic | Moderate |
| CAPTCHA Solving | Built-in (98% success rate) Supports reCAPTCHA, Cloudflare Turnstile/Challenge, AWS WAF, DataDome, etc. |
External dependency | External dependency |
At the same time, Scrapeless performs better than other competing products in high-concurrency scenarios. The following is a summary of its capabilities from different dimensions:
| Feature / Platform | Scrapeless | Browserless | Browserbase | HyperBrowser | Bright Data | ZenRows | Steel.dev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment Method | Cloud-based | Cloud-based Puppeteer containers | Multi-browser cloud cluster | Cloud-based headless browser platform | Cloud deployment | Browser API interface | Browser cloud cluster + Browser API |
| Concurrency Support | 50 to Unlimited | 3–50 | 3–50 | 1–250 | Up to unlimited (depending on plan) | Up to 100 (Business plan) | No official data |
| Anti-Detection Capability | Free CAPTCHA recognition & bypass, supports reCAPTCHA, Cloudflare Turnstile/Challenge, AWS WAF, DataDome, etc. | CAPTCHA bypass | CAPTCHA bypass + Incognito Mode | CAPTCHA bypass + Incognito + Session Mgmt | CAPTCHA bypass + Fingerprint spoofing + Proxy | Custom browser fingerprints | Proxy + Fingerprint recognition |
| Browser Runtime Cost | $0.063 – $0.090/hour (includes free CAPTCHA bypass) | $0.084 – $0.15/hour (unit-based) | $0.10 – $0.198/hour (includes 2–5GB free proxy) | $30–$100/month | ~$0.10/hour | ~$0.09/hour | $0.05 – $0.08/hour |
| Proxy Cost | $1.26 – $1.80/GB | $4.3/GB | $10/GB (beyond free quota) | No official data | $9.5/GB (standard); $12.5/GB (premium domains) | $2.8 – $5.42/GB | $3 – $8.25/GB |
2.3 CAPTCHA automatic solution and event monitoring mechanism
Scrapeless provides advanced CAPTCHA solutions and extends a series of custom functions through Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP) to enhance the reliability of browser automation.
CAPTCHA solving ability
Scrapeless can automatically handle mainstream CAPTCHA types, including: reCAPTCHA, Cloudflare Turnstile/Challange, AWS WAF, DataDome, etc.
Event monitoring mechanism
Scrapeless provides three core events for monitoring the CAPTCHA solving process:
| Event Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Captcha.detected | CAPTCHA detected |
| Captcha.solveFinished | CAPTCHA solved |
| Captcha.solveFailed | CAPTCHA solving failed |
Event Response Data Structure
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | string | CAPTCHA type (e.g., recaptcha, turnstile) |
| success | boolean | Result of solving |
| message | string | Status message (e.g., "NOT_DETECTED", "SOLVE_FINISHED") |
| token? | string | Returned token upon success (optional) |
2.4 Powerful proxy support
Scrapeless provides a flexible and controllable proxy integration system that supports multiple proxy modes:
- Built-in residential proxy: supports geographic proxy in 195 countries/regions around the world, out of the box.
- Custom proxy (premium subscription): allows users to connect to their own proxy service, which is not included in Scrapeless's proxy billing.
2.5 Session replay
Session replay is one of the most powerful features of Scrapeless Scraping Browser. It allows you to replay the session page by page to check the operations and network requests performed.
3. Code example: Scrapeless integration and use
3.1 Use of Scrapeless Scraping Browser
Puppeteer example
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-core');
const connectionURL = 'wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?token=your-scrapeless-api-key&session_ttl=180&proxy_country=ANY';
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({browserWSEndpoint: connectionURL});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.scrapeless.com');
console.log(await page.title());
await browser.close();
})();Playwright Example
const {chromium} = require('playwright-core');
const connectionURL = 'wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?token=your-scrapeless-api-key&session_ttl=180&proxy_country=ANY';
(async () => {
const browser = await chromium.connectOverCDP(connectionURL);
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.scrapeless.com');
console.log(await page.title());
await browser.close();
})();3.2 Scrapeless Scraping Browser Fingerprint Parameters Example Code
The following is a simple example code showing how to integrate Scrapeless's browser fingerprint customization function through Puppeteer and Playwright:
Puppeteer Example
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-core');
// custom browser fingerprint
const fingerprint = {
userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/134.1.2.3 Safari/537.36',
platform: 'Windows',
screen: {
width: 1280, height: 1024
},
localization: {
languages: ['zh-HK', 'en-US', 'en'], timezone: 'Asia/Hong_Kong',
}
}
const query = new URLSearchParams({
token: 'APIKey', // required
session_ttl: 180,
proxy_country: 'ANY',
fingerprint: encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify(fingerprint)),
});
const connectionURL = `wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?${query.toString()}`;
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({browserWSEndpoint: connectionURL});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.scrapeless.com');
const info = await page.evaluate(() => {
return {
screen: {
width: screen.width,
height: screen.height,
},
userAgent: navigator.userAgent,
timeZone: Intl.DateTimeFormat().resolvedOptions().timeZone,
languages: navigator.languages
};
});
console.log(info);
await browser.close();
})();
Playwright Example
const { chromium } = require('playwright-core');
// custom browser fingerprint
const fingerprint = {
userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/134.1.2.3 Safari/537.36',
platform: 'Windows',
screen: {
width: 1280, height: 1024
},
localization: {
languages: ['zh-HK', 'en-US', 'en'], timezone: 'Asia/Hong_Kong',
}
}
const query = new URLSearchParams({
token: 'APIKey', // required
session_ttl: 180,
proxy_country: 'ANY',
fingerprint: encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify(fingerprint)),
});
const connectionURL = `wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?${query.toString()}`;
(async () => {
const browser = await chromium.connectOverCDP(connectionURL);
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.scrapeless.com');
const info = await page.evaluate(() => {
return {
screen: {
width: screen.width,
height: screen.height,
},
userAgent: navigator.userAgent,
timeZone: Intl.DateTimeFormat().resolvedOptions().timeZone,
languages: navigator.languages
};
});
console.log(info);
await browser.close();
})();
3.3 CAPTCHA event monitoring example
The following is a complete code example of using Scrapeless to monitor CAPTCHA events, showing how to monitor the solution status of CAPTCHA in real time:
// Listen for CAPTCHA solving events
const client = await page.createCDPSession();
client.on('Captcha.detected', (result) => {
console.log('Captcha detected:', result);
});
await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
client.on('Captcha.solveFinished', (result) => {
if (result.success) resolve();
});
client.on('Captcha.solveFailed', () =>
reject(new Error('Captcha solve failed'))
);
setTimeout(() =>
reject(new Error('Captcha solve timeout')),
5 * 60 * 1000
);
});After mastering the core features and advantages of Scrapeless Scraping Browser, we can not only better understand its value in modern web scraping but also leverage its performance advantages more effectively. To help developers automate and scrape websites more efficiently and securely, we will now explore how to apply Scrapeless Scraping Browser in specific use cases, based on common scenarios.
4. Best Practices for Automation and Web Scraping Using Scrapeless Scraping Browser
Legal Disclaimer and Precautions
This tutorial covers popular web scraping techniques for education. Interacting with public servers requires diligence and respect and here's a good summary of what not to do:
- Do not scrape at rates that could damage the website.
- Do not scrape data that's not available publicly.
- Do not store PII of EU citizens who are protected by GDPR.
- Do not repurpose the entire public datasets which can be illegal in some countries.
Understanding Cloudflare Protection
- What is Cloudflare?
Cloudflare is a cloud platform that integrates content delivery network (CDN), DNS acceleration, and security protection. Websites use Cloudflare to mitigate Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks (i.e., websites going offline due to multiple access requests) and ensure that websites using it are always operational.
Here’s a simple example to understand how Cloudflare works:
When you visit a website that has Cloudflare enabled (such as example.com), your request first reaches Cloudflare’s edge server, not the origin server. Cloudflare will then determine whether to allow your request to continue based on several rules, such as:
- Whether the cached page can be returned directly;
- Whether you need to pass a CAPTCHA test;
- Whether your request will be blocked;
- Whether the request will be forwarded to the actual website server (origin).
If you are identified as a legitimate user, Cloudflare will forward the request to the origin server and return the content to you. This mechanism greatly enhances the website's security but also presents significant challenges for automated access.
Bypassing Cloudflare is one of the toughest technical challenges in many data collection tasks. Below, we will dive deeper into why bypassing Cloudflare is difficult.
- Challenges in Bypassing Cloudflare Protection
Bypassing Cloudflare is not easy, especially when advanced anti-bot features (such as Bot Management, Managed Challenge, Turnstile Verification, JS challenges, etc.) are enabled. Many traditional scraping tools (like Selenium and Puppeteer) are often detected and blocked before requests are even made due to obvious fingerprint features or unnatural behavior simulations.
Although there are some open-source tools specifically designed to bypass Cloudflare (such as FlareSolverr, undetected-chromedriver), these tools typically have a short lifespan. Once they are widely used, Cloudflare quickly updates its detection rules to block them. This means that to bypass Cloudflare's protection mechanisms in a sustained and stable manner, teams often need in-house development capabilities and continuous resource investment for maintenance and updates.
Here are the main challenges in bypassing Cloudflare protection:
- Strict Browser Fingerprint Recognition: Cloudflare detects fingerprint features in requests such as User-Agent, language settings, screen resolution, time zone, and Canvas/WebGL rendering. If it detects abnormal browsers or automation behaviors, it blocks the request.
- Complex JS Challenge Mechanisms: Cloudflare dynamically generates JavaScript challenges (such as CAPTCHA, delayed redirects, logical calculations, etc.), and automated scripts often struggle to correctly parse or execute these complex logics.
- Behavioral Analysis Systems: In addition to static fingerprints, Cloudflare also analyzes user behavior trajectories, such as mouse movements, time spent on a page, scrolling actions, etc. This requires high precision in simulating human behavior.
- Rate and Concurrency Control: High-frequency access can easily trigger Cloudflare’s rate limiting and IP blocking strategies. Proxy pools and distributed scheduling must be highly optimized.
- Invisible Server-Side Validation: Since Cloudflare is an edge interceptor, many real requests are blocked before reaching the origin server, making traditional packet capture analysis methods ineffective.
Therefore, successfully bypassing Cloudflare requires simulating real browser behavior, executing JavaScript dynamically, configuring fingerprints flexibly, and using high-quality proxies and dynamic scheduling mechanisms.
Bypassing Idealista Cloudflare with Scrapeless Scraping Browser to Collect Real Estate Data
In this chapter, we will demonstrate how to use Scrapeless Scraping Browser to build an efficient, stable, and anti-anti-scraping automation system for scraping real estate data from Idealista, a leading European real estate platform. Idealista employs multiple protection mechanisms, including Cloudflare, dynamic loading, IP rate limiting, and user behavior recognition, making it a highly challenging target platform.
We will focus on the following technical aspects:
- Bypassing Cloudflare verification pages
- Custom fingerprinting and simulating real user behavior
- Using Session Replay
- High-concurrency scraping with multiple proxy pools
- Cost optimization
Understanding the Challenge: Idealista's Cloudflare Protection
Idealista is a leading online real estate platform in Southern Europe, offering millions of listings for various types of properties, including residential homes, apartments, and shared rooms. Given the highly commercial value of its property data, the platform has implemented strict anti-scraping measures.
To combat automated scraping, Idealista has deployed Cloudflare — a widely used anti-bot and security protection system designed to defend against malicious bots, DDoS attacks, and data abuse. Cloudflare's anti-scraping mechanisms primarily consist of the following elements:
- Access Verification Mechanisms: Including JS Challenge, browser integrity checks, and CAPTCHA verification, to determine whether the visitor is a real user.
- Behavioral Analysis: Detecting real users through actions such as mouse movements, clicking patterns, and scroll speeds.
- HTTP Header Analysis: Inspecting browser types, language settings, and referrer data to check for discrepancies. Suspicious headers may expose attempts to disguise automated bots.
- Fingerprint Detection and Blocking: Identifying traffic generated by automation tools (like Selenium and Puppeteer) through browser fingerprints, TLS fingerprints, and header information.
- Edge Node Filtering: Requests first enter Cloudflare's global edge network, which evaluates their risk. Only requests deemed low-risk are forwarded to Idealista's origin servers.
Next, we will explain in detail how to use Scrapeless Scraping Browser to bypass Idealista's Cloudflare protection and successfully collect real estate data.
Bypassing Idealista Cloudflare with Scrapeless Scraping Browser
Prerequisites
Before we begin, let's make sure we have the necessary tools:
-
Python: If you haven't installed Python yet, please download the latest version and install it on your system.
-
Required Libraries: You need to install several Python libraries. Open a terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 lxml selenium selenium-wire undetected-chromedriver -
ChromeDriver: Download ChromeDriver. Make sure to choose the version that matches your installed version of Chrome.
-
Scrapeless Account: To bypass Idealista's bot protection, you’ll need a Scrapeless Scraping Browser account. You can sign up here and receive a $2 free trial.
Locating the Data
Our goal is to extract detailed information about each property listing on Idealista. We can use the browser’s developer tools to understand the structure of the site and identify the HTML elements we need to target.
Right-click anywhere on the page and select Inspect to view the page source.
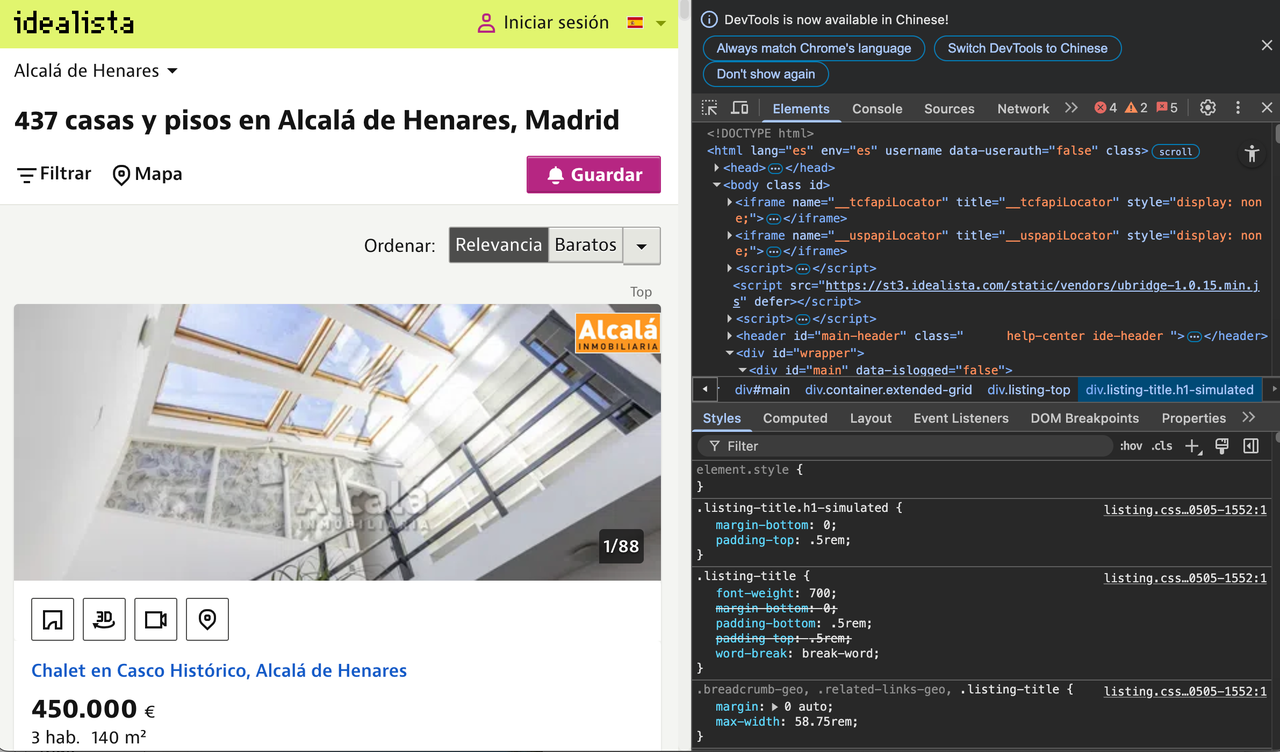
In this article, we will focus on scraping property listings from Alcala de Henares, Madrid using the following URL:
https://www.idealista.com/venta-viviendas/alcala-de-henares-madrid/
We want to extract the following data points from each listing:
- Title
- Price
- Area information
- Property description
- Image URLs
Below you can see the annotated property listing page showing where all the information for each property is located.
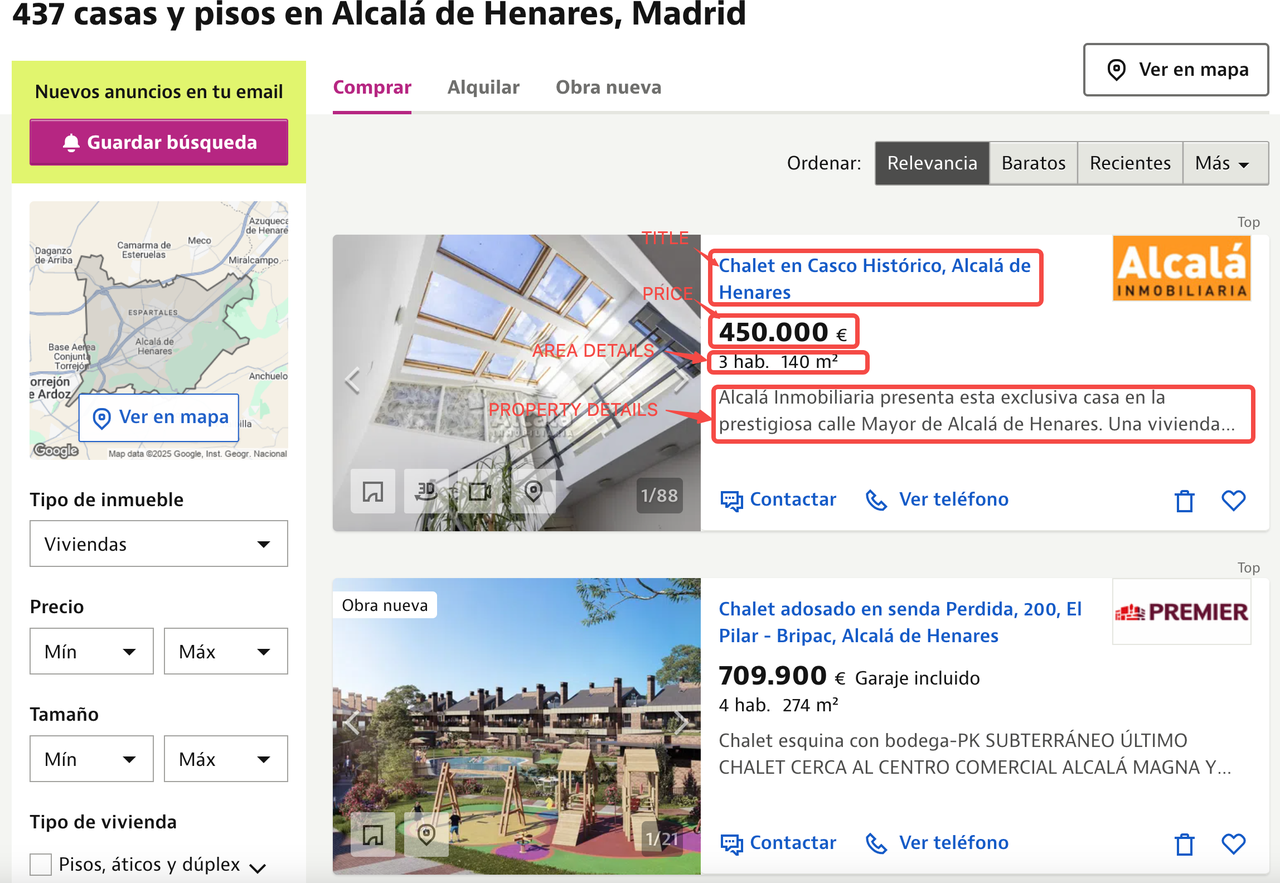
By inspecting the HTML source code, we can identify the CSS selector for each data point. CSS selectors are patterns used to select elements in an HTML document.
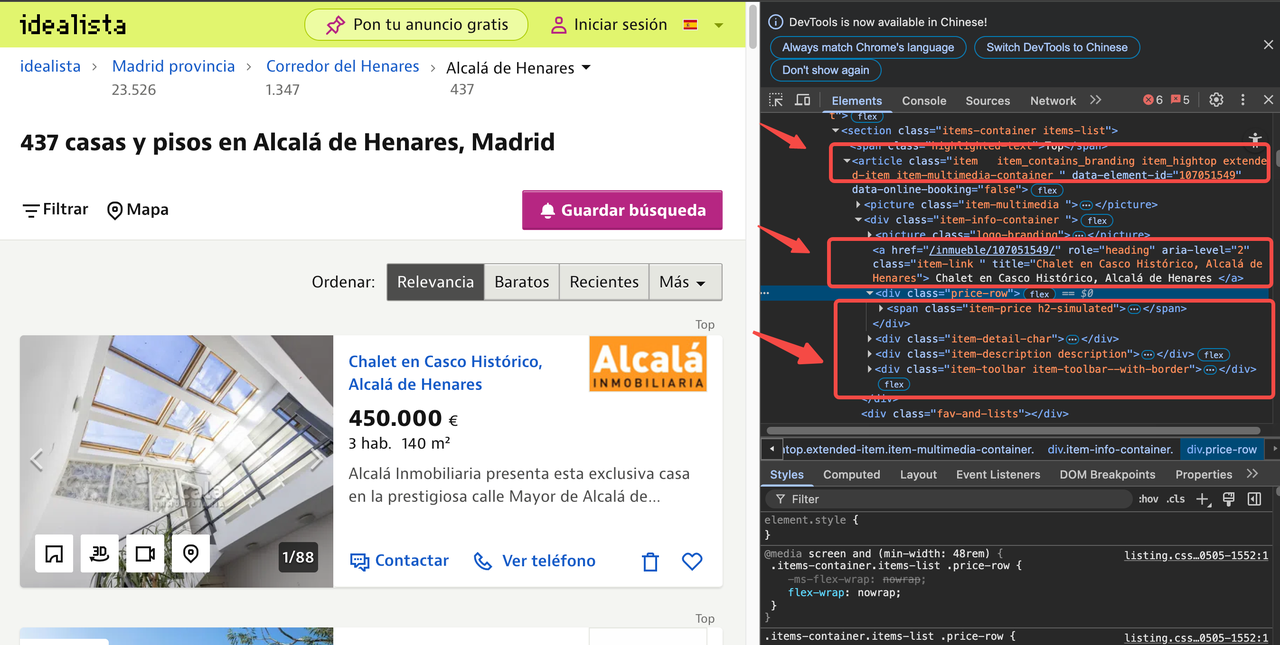
By inspecting the HTML source code, we found that each property listing is contained within an <article> tag with the class item. Within each item:
- The title is located in an
<a>tag with the classitem-link. - The price is found in a
<span>tag with the classitem-price. - And so on for other data points.
Step 1: Set Up Selenium with ChromeDriver
First, we need to configure Selenium to use ChromeDriver. Start by setting up chrome_options and initializing the ChromeDriver.
from seleniumwire import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
from datetime import datetime
import json
def listings(url):
chrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument("--headless")
s = Service("Replace with your path to ChromeDriver")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=s, chrome_options=chrome_options)This code imports the necessary modules, including seleniumwire for advanced browser interactions and BeautifulSoup for HTML parsing.
We define a function listings(url) and configure Chrome to run in headless mode by adding the --headless argument to chrome_options. Then, we initialize ChromeDriver using the specified service path.
Step 2: Load the Target URL
Next, we load the target URL and wait for the page to fully load.
driver.get(url)
time.sleep(8) # Adjust based on website's load timeHere, the driver.get(url) command instructs the browser to navigate to the specified URL.
We use time.sleep(8) to pause the script for 8 seconds, allowing enough time for the web page to fully load. This wait time can be adjusted depending on the website's loading speed.
Step 3: Parse the Page Content
Once the page is loaded, we use BeautifulSoup to parse its content:
soup = BeautifulSoup(driver.page_source, "lxml")
driver.quit()Here, we use driver.page_source to retrieve the HTML content of the loaded page, and parse it using BeautifulSoup with the lxml parser. Finally, we call driver.quit() to close the browser instance and clean up resources.
Step 4: Extract Data from the Parsed HTML
Next, we extract the relevant data from the parsed HTML.
house_listings = soup.find_all("article", class_="item")
extracted_data = []
for listing in house_listings:
description_elem = listing.find("div", class_="item-description")
description_text = description_elem.get_text(strip=True) if description_elem else "nil"
item_details = listing.find_all("span", class_="item-detail")
bedrooms = item_details[0].get_text(strip=True) if len(item_details) > 0 else "nil"
area = item_details[1].get_text(strip=True) if len(item_details) > 1 else "nil"
image_urls = [img["src"] for img in listing.find_all("img") if img.get("src")]
first_image_url = image_urls[0] if image_urls else "nil"
listing_info = {
"Title": listing.find("a", class_="item-link").get("title", "nil"),
"Price": listing.find("span", class_="item-price").get_text(strip=True),
"Bedrooms": bedrooms,
"Area": area,
"Description": description_text,
"Image URL": first_image_url,
}
extracted_data.append(listing_info)Here, we look for all elements matching the article tag with the class name item, which represent individual property listings. For each listing, we extract its title, details (such as number of bedrooms and area), and the image URL. We store these details in a dictionary and append each dictionary to a list called extracted_data.
Step 5: Save the Extracted Data
Finally, we save the extracted data into a JSON file.
current_datetime = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
json_filename = f"new_revised_data_{current_datetime}.json"
with open(json_filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as json_file:
json.dump(extracted_data, json_file, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"Extracted data saved to {json_filename}")
url = "https://www.idealista.com/venta-viviendas/alcala-de-henares-madrid/"
idealista_listings = listings(url)Here is the complete code:
from seleniumwire import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
from datetime import datetime
import json
def listings(url):
chrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument("--headless")
s = Service("Replace with your path to ChromeDriver")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=s, chrome_options=chrome_options)
driver.get(url)
time.sleep(8) # Adjust based on website's load time
soup = BeautifulSoup(driver.page_source, "lxml")
driver.quit()
house_listings = soup.find_all("article", class_="item")
extracted_data = []
for listing in house_listings:
description_elem = listing.find("div", class_="item-description")
description_text = description_elem.get_text(strip=True) if description_elem else "nil"
item_details = listing.find_all("span", class_="item-detail")
bedrooms = item_details[0].get_text(strip=True) if len(item_details) > 0 else "nil"
area = item_details[1].get_text(strip=True) if len(item_details) > 1 else "nil"
image_urls = [img["src"] for img in listing.find_all("img") if img.get("src")]
first_image_url = image_urls[0] if image_urls else "nil"
listing_info = {
"Title": listing.find("a", class_="item-link").get("title", "nil"),
"Price": listing.find("span", class_="item-price").get_text(strip=True),
"Bedrooms": bedrooms,
"Area": area,
"Description": description_text,
"Image URL": first_image_url,
}
extracted_data.append(listing_info)
current_datetime = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
json_filename = f"new_revised_data_{current_datetime}.json"
with open(json_filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as json_file:
json.dump(extracted_data, json_file, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"Extracted data saved to {json_filename}")
url = "https://www.idealista.com/venta-viviendas/alcala-de-henares-madrid/"
idealista_listings = listings(url)Bypassing Bot Detection
If you’ve run the script at least twice during this tutorial, you may have noticed that a CAPTCHA page appears.
The Cloudflare Challenge page initially loads the cf-chl-bypass script and performs JavaScript computations, which typically takes about 5 seconds.
Scrapeless offers a simple and reliable way to access data from sites like Idealista without having to build and maintain your own scraping infrastructure. The Scrapeless Scraping Browser is a high-concurrency automation solution built for AI. It’s a high-performance, cost-effective, anti-blocking browser platform designed for large-scale data scraping and simulates highly human-like behavior. It can handle reCAPTCHA, Cloudflare Turnstile/Challenge, AWS WAF, DataDome, and more in real time, making it an efficient web scraping solution.
Below are the steps to bypass Cloudflare protection using Scrapeless:
Step 1: Preparation
1.1 Create a Project Folder
- Create a new folder for your project, for example,
scrapeless-bypass. - Navigate to the folder in your terminal:
cd path/to/scrapeless-bypass1.2 Initialize the Node.js project
Run the following command to create the package.json file:
npm init -y1.3 Install required dependencies
Install Puppeteer-core, which allows remote connections to the browser instance:
npm install puppeteer-coreIf Puppeteer is not already installed on your system, install the full version:
npm install puppeteer puppeteer-coreStep 2: Get Your Scrapeless API Key
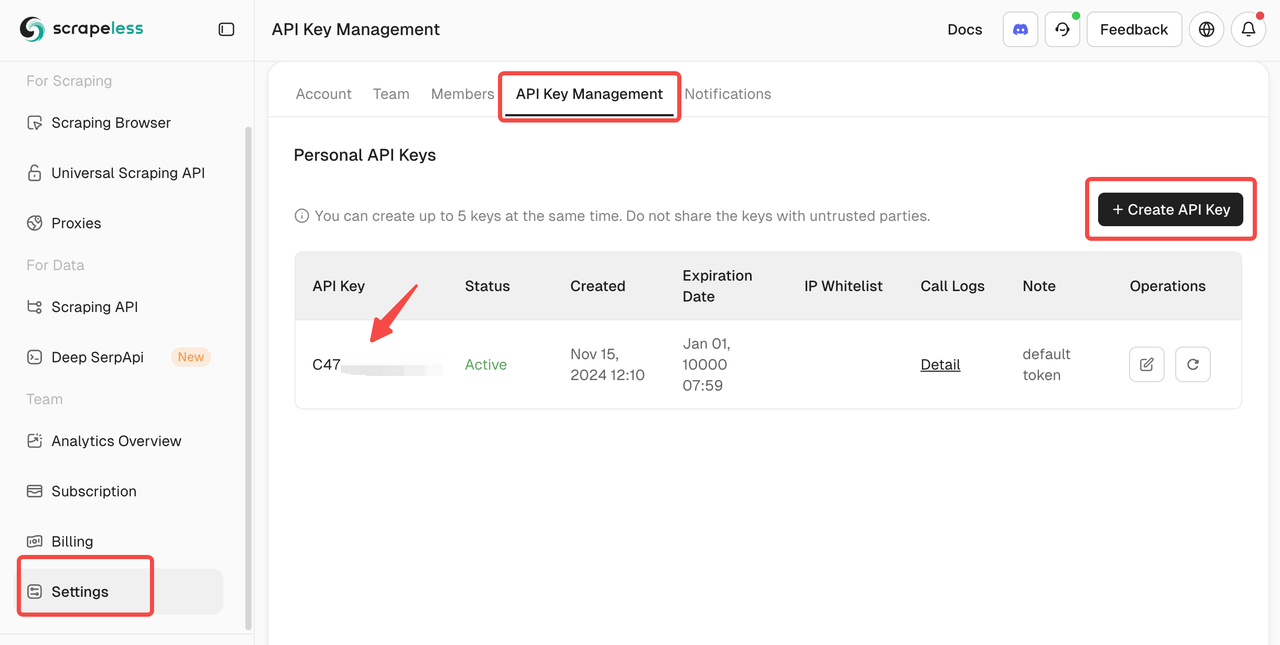
2.1 Sign Up on Scrapeless
- Go to Scrapeless and create an account.
- Navigate to the API Key Management section.
- Generate a new API key and copy it.
Step 3: Connect to Scrapeless Browserless
3.1 Get the WebSocket connection URL
Scrapeless provides Puppeteer with a WebSocket connection URL to interact with the cloud-based browser.
The format is:
wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?token=APIKey&session_ttl=180&proxy_country=ANYReplace APIKey with your actual Scrapeless API key.
3.2 Configure Connection Parameters
token: Your Scrapeless API keysession_ttl: Duration of the browser session (in seconds), e.g.,180proxy_country: Country code of the proxy server (e.g.,GBfor the United Kingdom,USfor the United States)
Step 4: Write the Puppeteer Script
4.1 Create the Script File
Inside your project folder, create a new JavaScript file named bypass-cloudflare.js.
4.2 Connect to Scrapeless and Launch Puppeteer
Add the following code to bypass-cloudflare.js:
import puppeteer from 'puppeteer-core';
const API_KEY = 'your_api_key'; // Replace with your actual API Keyconst host = 'wss://browser.scrapeless.com';
const query = new URLSearchParams({token: API_KEY,session_ttl: '180', // Browser session duration in secondsproxy_country: 'GB', // Proxy country codeproxy_session_id: 'test_session', // Proxy session ID (keeps the same IP)proxy_session_duration: '5' // Proxy session duration in minutes
}).toString();
const connectionURL = `${host}/browser?${query}`;
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({browserWSEndpoint: connectionURL,defaultViewport: null,
});
console.log('Connected to Scrapeless');4.3 Open a webpage and bypass Cloudflare
Extend the script to open a new page and navigate to a website protected by Cloudflare:
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.scrapingcourse.com/cloudflare-challenge', { waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded' });4.4 Waiting for page elements to load
Make sure Cloudflare protection is bypassed before proceeding:
await page.waitForSelector('main.page-content .challenge-info', { timeout: 30000 }); // Adjust selector as needed4.5 Take a screenshot
To verify whether Cloudflare protection has been successfully bypassed, take a screenshot of the page:
await page.screenshot({ path: 'challenge-bypass.png' });
console.log('Screenshot saved as challenge-bypass.png');4.6 Complete script
The following is the complete script:
import puppeteer from 'puppeteer-core';
const API_KEY = 'your_api_key'; // Replace with your actual API Key
const host = 'wss://browser.scrapeless.com';
const query = new URLSearchParams({
token: API_KEY,
session_ttl: '180',
proxy_country: 'GB',
proxy_session_id: 'test_session',
proxy_session_duration: '5'
}).toString();
const connectionURL = `${host}/browser?${query}`;
(async () => {
try {
// Connect to Scrapeless
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: connectionURL,
defaultViewport: null,
});
console.log('Connected to Scrapeless');
// Open a new page and navigate to the target website
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.scrapingcourse.com/cloudflare-challenge', { waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded' });
// Wait for the page to load completely
await page.waitForTimeout(5000); // Adjust delay if necessary
await page.waitForSelector('main.page-content', { timeout: 30000 });
// Capture a screenshot
await page.screenshot({ path: 'challenge-bypass.png' });
console.log('Screenshot saved as challenge-bypass.png');
// Close the browser
await browser.close();
console.log('Browser closed');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
}
})();Step 5: Run the script
5.1 Save the script
Make sure the script is saved as bypass-cloudflare.js.
5.2 Execute the script
Run the script using Node.js:
node bypass-cloudflare.js5.3 Expected Output
If everything is set up correctly, the terminal will display:
Connected to Scrapeless
Screenshot saved as challenge-bypass.png
Browser closedThe challenge-bypass.png file will appear in your project folder, confirming that Cloudflare protection has been successfully bypassed.
You can also integrate Scrapeless Scraping Browser directly into your scraping code:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-core');
const connectionURL = 'wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?token=C4778985476352D77C08ECB031AF0857&session_ttl=180&proxy_country=ANY';
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({browserWSEndpoint: connectionURL});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.scrapeless.com');
console.log(await page.title());
await browser.close();
})();Fingerprint Customization
When scraping data from websites—especially large real estate platforms like Idealista—even if you successfully bypass Cloudflare challenges using Scrapeless, you might still be flagged as a bot due to repetitive or high-volume access.
Websites often use browser fingerprinting to detect automated behavior and restrict access.
⚠️ Common Issues You May Encounter
-
Slow response times after multiple scrapes
The site may throttle requests based on IP or behavioral patterns. -
Page layout fails to render
Dynamic content may rely on real browser environments, causing missing or broken data during scraping. -
Missing listings in certain regions
Websites may block or hide content based on suspicious traffic patterns.
These problems are usually caused by identical browser configurations for each request. If your browser fingerprint remains unchanged, it’s easy for anti-bot systems to detect automation.
Solution: Custom Fingerprinting with Scrapeless
Scrapeless Scraping Browser provides built-in support for fingerprint customization to mimic real user behavior and avoid detection.
You can randomize or customize the following fingerprint elements:
| Fingerprint Element | Description |
|---|---|
| User-Agent | Mimic various OS/browser combinations (e.g., Chrome on Windows/Mac). |
| Platform | Simulate different operating systems (Windows, macOS, etc.). |
| Screen Size | Emulate various device resolutions to avoid mobile/desktop mismatches. |
| Localization | Align language and timezone with geolocation for consistency. |
By rotating or customizing these values, each request appears more natural—reducing the risk of detection and improving data extraction reliability.
Code example:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-core');
const query = new URLSearchParams({
token: 'your-scrapeless-api-key', // required
session_ttl: 180,
proxy_country: 'ANY',
// Set fingerprint parameters
userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/134.0.6998.45 Safari/537.36',
platform: 'Windows',
screen: JSON.stringify({ width: 1280, height: 1024 }),
localization: JSON.stringify({
locale: 'zh-HK',
languages: ['zh-HK', 'en-US', 'en'],
timezone: 'Asia/Hong_Kong',
})
});
const connectionURL = `wss://browser.Scrapeless.com/browser?${query.toString()}`;
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({browserWSEndpoint: connectionURL});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.Scrapeless.com');
console.log(await page.title());
await browser.close();
})();
Session Replay
After customizing browser fingerprints, page stability significantly improves, and content extraction becomes more reliable.
However, during large-scale scraping operations, unexpected issues may still cause extraction failures. To address this, Scrapeless offers a powerful Session Replay feature.
What is Session Replay?
Session Replay records the entire browser session in detail, capturing all interactions, such as:
- Page load process
- Network request and response data
- JavaScript execution behavior
- Dynamically loaded but unparsed content
Why Use Session Replay?
When scraping complex websites like Idealista, Session Replay can greatly improve debugging efficiency.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Precise Issue Tracking | Quickly identify failed requests without guesswork |
| No Need to Re-run Code | Analyze issues directly from the replay instead of rerunning the scraper |
| Improved Collaboration | Share replay logs with team members for easier troubleshooting |
| Dynamic Content Analysis | Understand how dynamically loaded data behaves during scraping |
Usage Tip
Once Session Replay is enabled, check the replay logs first whenever a scrape fails or data looks incomplete. This helps you diagnose the issue faster and reduce debugging time.
Proxy Configuration
When scraping Idealista, it's important to note that the platform is highly sensitive to non-local IP addresses—especially when accessing listings from specific cities. If your IP originates from outside the country, Idealista may:
- Block the request entirely
- Return a simplified or stripped-down version of the page
- Serve empty or incomplete data, even without triggering a CAPTCHA
Scrapeless Built-in Proxy Support
Scrapeless offers built-in proxy configuration, allowing you to specify your geographic source directly.
You can configure this using either:
proxy_country: A two-letter country code (e.g.,'ES'for Spain)proxy_url: Your own proxy server URL
Example usage:
proxy_country: 'ES',High Concurrency
The page we just scraped from Idealista—Alcalá de Henares Real Estate Listings—has as many as 6 pages of listings.
When you're researching industry trends or gathering competitive marketing strategies, you might need to scrape real estate data from 20+ cities daily, covering thousands of pages. In some cases, you may even need to refresh this data every hour.
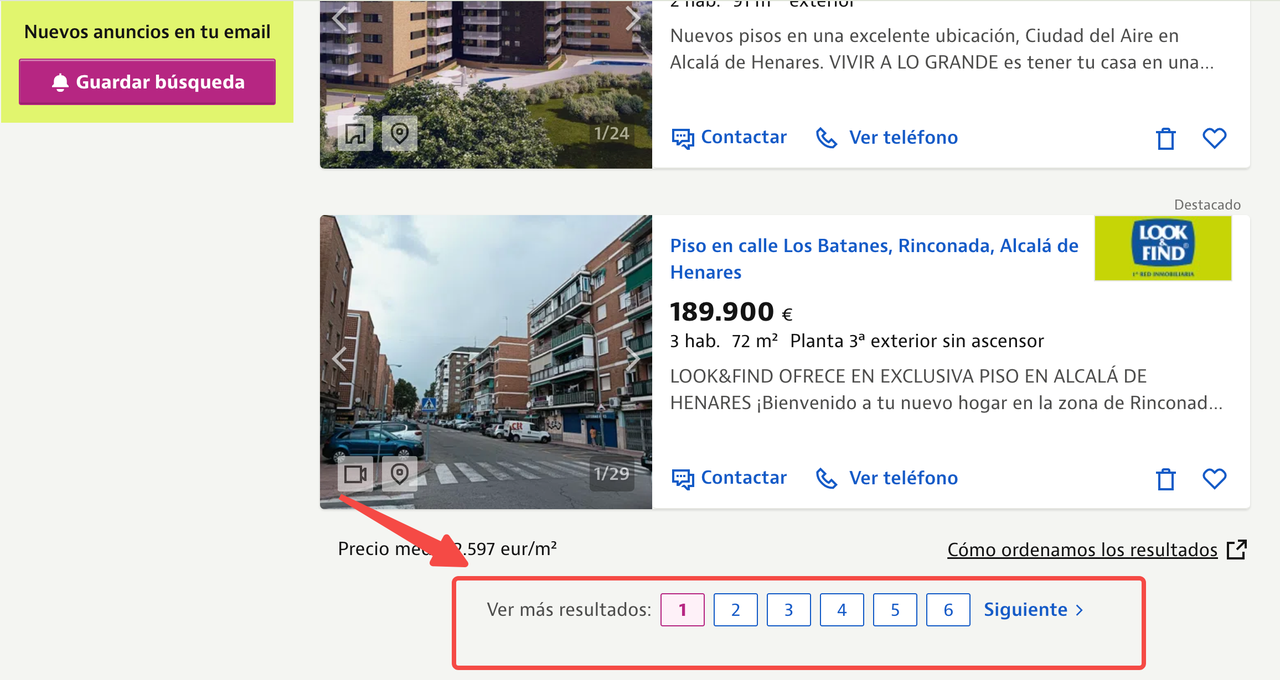
High-Concurrency Requirements
To handle this volume efficiently, consider the following requirements:
- Multiple concurrent connections: To scrape data from hundreds of pages without long wait times.
- Automation tools: Use Scrapeless Scraping Browser or similar tools that can handle concurrent requests at scale.
- Session management: Maintain persistent sessions to avoid excessive CAPTCHAs or IP blocks.
Scrapeless Scalability
Scrapeless is specifically designed for high-concurrency scraping. It offers:
- Parallel browser sessions: Handle multiple requests simultaneously, allowing you to scrape large amounts of data across many cities.
- Low-cost, high-efficiency scraping: Scraping in parallel reduces the cost per page scraped while optimizing throughput.
- Bypass high-volume anti-bot defenses: Automatically handles CAPTCHA and other verification systems, even during high-load scraping.
Tip: Ensure your requests are spaced out enough to mimic human-like browsing behavior and prevent rate-limiting or bans from Idealista.
Scalability & Cost Efficiency
Regular Puppeteer struggles to efficiently scale sessions and integrate with queuing systems. However, Scrapeless Scraping Browser supports seamless scaling from dozens of concurrent sessions to unlimited concurrent sessions, ensuring zero queue time and zero timeouts even during peak task loads.
Here’s a comparison of various tools for high-concurrency scraping. Even with Scrapeless' high-concurrency browser, you don’t need to worry about costs—in fact, it can help you save nearly 50% in fees.
Tool Comparison
| Tool Name | Hourly Rate (USD/hour) | Proxy Fees (USD/GB) | Concurrent Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scrapeless | $0.063 – $0.090/hour (depends on concurrency & usage) | $1.26 – $1.80/GB | 50 / 100 / 200 / 400 / 600 / 1000 / Unlimited |
| Browserbase | $0.10 – $0.198/hour (includes 2-5GB free proxies) | $10/GB (after the free allocation) | 3 (Basic) / 50 (Advanced) |
| Brightdata | $0.10/hour | $9.5/GB (Standard); $12.5/GB (Advanced domains) | Unlimited |
| Zenrows | $0.09/hour | $2.8 – $5.42/GB | Up to 100 |
| Browserless | $0.084 – $0.15/hour (unit-based billing) | $4.3/GB | 3 / 10 / 50 |
Tip: If you require massive-scale scraping and high-concurrency support, Scrapeless offers the best cost-to-performance ratio.
Cost Control Strategies for Web Scraping
Careful users may have noticed that the Idealista pages we scrape often contain large amounts of high-definition property images, interactive maps, video presentations, and ad scripts. While these elements are user-friendly for end users, they are unnecessary for data extraction and significantly increase bandwidth consumption and costs.
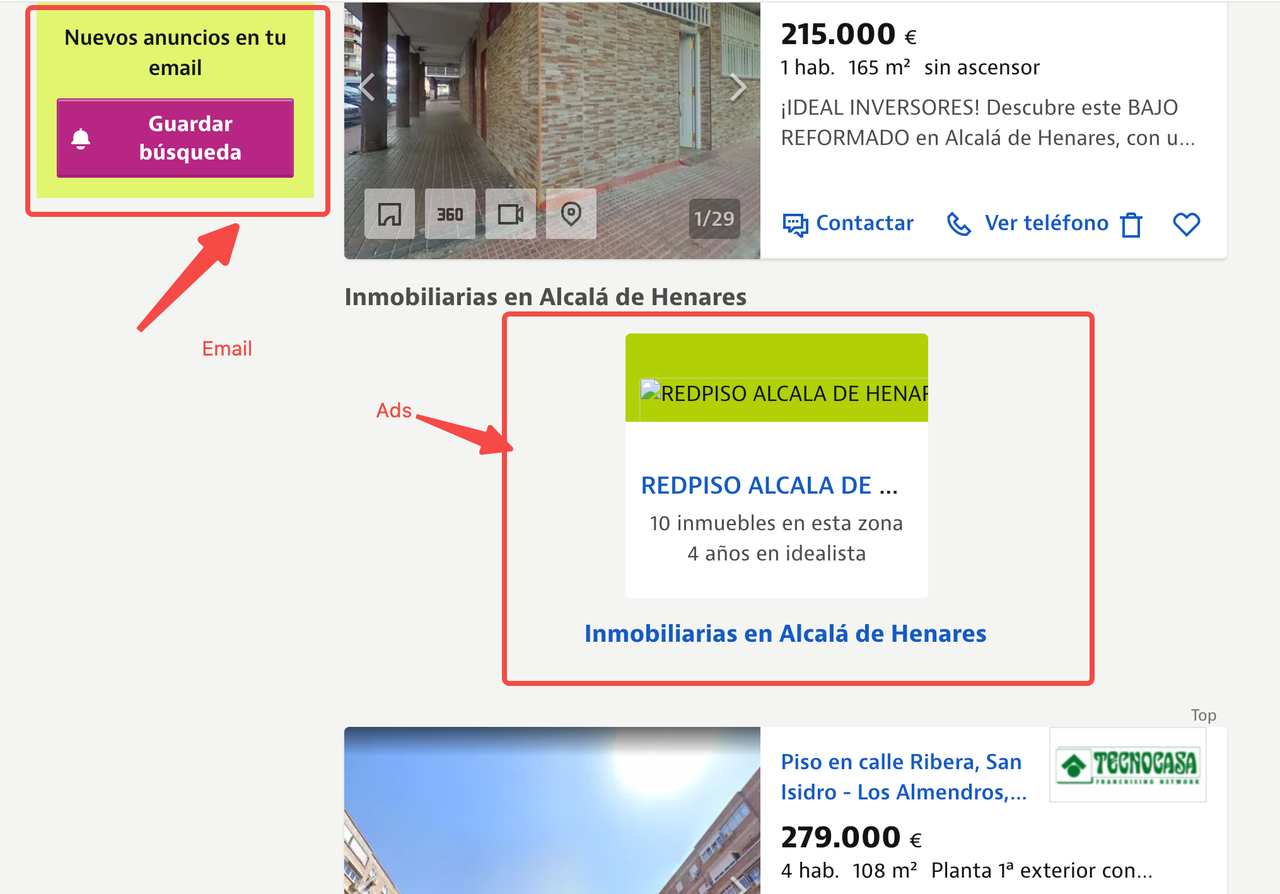
To optimize traffic usage, we recommend users employ the following strategies:
- Resource Interception: Intercept unnecessary resource requests to reduce traffic consumption.
- Request URL Interception: Intercept specific requests based on URL characteristics to further minimize traffic.
- Simulate Mobile Devices: Use mobile device configurations to fetch lighter page versions.
Detailed Strategies
1. Resource Interception
Enabling resource interception can significantly improve scraping efficiency. By configuring Puppeteer's setRequestInterception function, we can block resources such as images, media, fonts, and stylesheets, avoiding large content downloads.
2. Request URL Filtering
By examining request URLs, we can filter out irrelevant requests like advertising services and third-party analytics scripts that are unrelated to the data extraction. This reduces unnecessary network traffic.
3. Simulating Mobile Devices
Simulating a mobile device (e.g., setting the user agent to an iPhone) allows you to fetch a lighter, mobile-optimized version of the page. This results in fewer resources being loaded and speeds up the scraping process.
For more information, please refer to the Scrapeless official documentation
Example Code
Here’s an example of combining these three strategies using Scrapeless Cloud Browser + Puppeteer for optimized resource scraping:
import puppeteer from 'puppeteer-core';
const scrapelessUrl = 'wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?token=your_api_key&session_ttl=180&proxy_country=ANY';
async function scrapeWithResourceBlocking(url) {
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: scrapelessUrl,
defaultViewport: null
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
// Enable request interception
await page.setRequestInterception(true);
// Define resource types to block
const BLOCKED_TYPES = new Set([
'image',
'font',
'media',
'stylesheet',
]);
// Intercept requests
page.on('request', (request) => {
if (BLOCKED_TYPES.has(request.resourceType())) {
request.abort();
console.log(`Blocked: ${request.resourceType()} - ${request.url().substring(0, 50)}...`);
} else {
request.continue();
}
});
await page.goto(url, {waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded'});
// Extract data
const data = await page.evaluate(() => {
return {
title: document.title,
content: document.body.innerText.substring(0, 1000)
};
});
await browser.close();
return data;
}
// Usage
scrapeWithResourceBlocking('https://www.scrapeless.com')
.then(data => console.log('Scraping result:', data))
.catch(error => console.error('Scraping failed:', error));In this way, you can not only save high traffic costs, but also speed up the crawling speed while ensuring data quality, thereby improving the overall stability and efficiency of the system.
5. Security and Compliance Recommendations
When using Scrapeless for data scraping, developers should pay attention to the following:
- Comply with the target website's
robots.txtfile and relevant laws and regulations: Ensure that your scraping activities are legal and respect the site's guidelines. - Avoid excessive requests that could lead to website downtime: Be mindful of scraping frequency to prevent server overload.
- Do not scrape sensitive information: Do not collect user privacy data, payment information, or any other sensitive content.
6. Conclusion
In the age of big data, data collection has become a crucial foundation for digital transformation across industries. Especially in fields such as market intelligence, e-commerce price comparison, competitive analysis, financial risk management, and real estate analysis, the demand for data-driven decision-making has become increasingly urgent. However, with the continuous evolution of web technologies, particularly the widespread use of dynamically loaded content, traditional web scrapers are gradually revealing their limitations. These limitations not only make scraping more difficult but also lead to the escalation of anti-scraping mechanisms, raising the barrier for web scraping.
With the advancement of web technologies, traditional scrapers can no longer meet complex scraping needs. Below are some key challenges and corresponding solutions:
- Dynamic Content Loading: Browser-based scrapers, by simulating real browser rendering of JavaScript content, ensure they can scrape dynamically loaded web data.
- Anti-Scraping Mechanisms: Using proxy pools, fingerprint recognition, behavior simulation, and other techniques, we can bypass the anti-scraping mechanisms commonly triggered by traditional scrapers.
- High-Concurrency Scraping: Headless browsers support high-concurrency task deployment, paired with proxy scheduling, to meet the needs of large-scale data scraping.
- Compliance Issues: By using legal APIs and proxy services, scraping activities can be ensured to comply with the terms of the target websites.
As a result, browser-based scrapers have become the new trend in the industry. This technology not only simulates user behavior through real browsers but also flexibly handles modern websites' complex structures and anti-scraping mechanisms, offering developers more stable and efficient scraping solutions.
Scrapeless Scraping Browser embraces this technological trend by combining browser rendering, proxy management, anti-detection technologies, and high-concurrency task scheduling, helping developers efficiently and stably complete data scraping tasks in complex online environments. It improves scraping efficiency and stability through several core advantages:
- High-Concurrency Browser Solutions: Scrapeless supports large-scale, high-concurrency tasks, enabling rapid deployment of thousands of scraping tasks to meet long-term scraping demands.
- Anti-Detection as a Service: Built-in CAPTCHA Solvers and customizable fingerprints help developers bypass fingerprint and behavior recognition mechanisms, greatly reducing the risk of being blocked.
- Visual Debugging Tool - Session Replay: By replaying each browser interaction during the scraping process, developers can easily debug and diagnose issues in the scraping process, especially for handling complex pages and dynamically loaded content.
- Compliance and Transparency Assurance: Scrapeless emphasizes compliant data scraping, supporting adherence to website
robots.txtrules and providing detailed scraping logs to ensure that users' data scraping activities comply with target websites' policies. - Flexible Scalability: Scrapeless integrates seamlessly with Puppeteer, allowing users to customize their scraping strategies and connect with other tools or platforms for a one-stop data scraping and analysis workflow.
Whether scraping e-commerce platforms for price comparisons, extracting real estate website data, or applying it in financial risk monitoring and market intelligence analysis, Scrapeless provides high-efficiency, intelligent, and reliable solutions for various industries.
With the technical details and best practices covered in this article, you now understand how to leverage Scrapeless for large-scale data scraping. Whether handling dynamic pages, extracting complex interactive data, optimizing traffic usage, or overcoming anti-scraping mechanisms, Scrapeless helps you achieve your scraping goals swiftly and efficiently.
At Scrapeless, we only access publicly available data while strictly complying with applicable laws, regulations, and website privacy policies. The content in this blog is for demonstration purposes only and does not involve any illegal or infringing activities. We make no guarantees and disclaim all liability for the use of information from this blog or third-party links. Before engaging in any scraping activities, consult your legal advisor and review the target website's terms of service or obtain the necessary permissions.



